Capnography is a vital tool in emergency medical services (EMS). It significantly enhances patient care by providing real-time respiratory data. This technology helps EMTs monitor ventilation, circulation, and metabolism effectively. Incorporating capnography in EMS presents numerous benefits and challenges. This article explores these aspects in detail to offer a comprehensive understanding of capnography’s role in EMS.
Understanding Capnography
Definition and Function
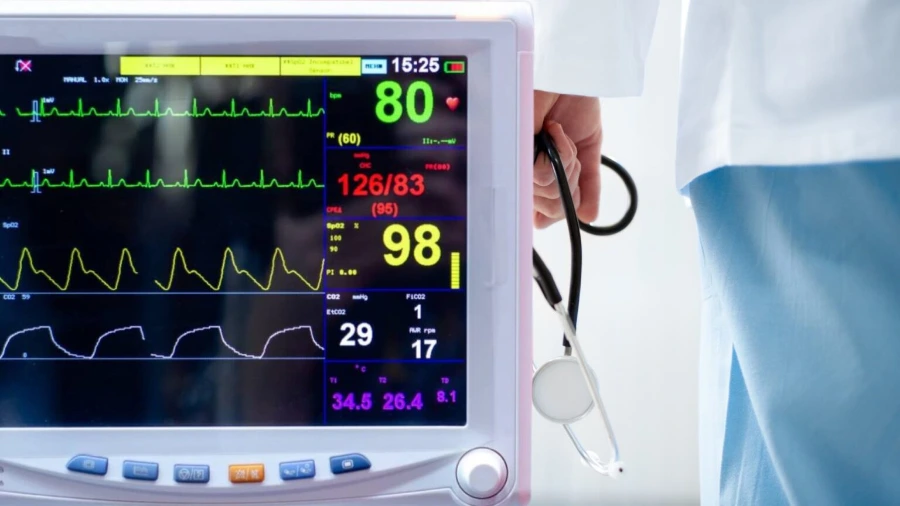
Capnography measures the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in exhaled air. This measurement provides crucial insights into a patient’s respiratory status. Capnography works by capturing exhaled air through sensors placed near the patient’s airway. It displays CO2 levels, helping EMTs assess ventilation, circulation, and metabolism. By understanding these parameters, EMTs can make informed decisions about patient care.
Types of Capnography
Waveform capnography displays CO2 levels as a continuous graph, showing the respiratory cycle’s phases. This type is especially useful for identifying trends and patterns in a patient’s breathing. Numeric capnography, on the other hand, provides a straightforward number representing the CO2 level. Both types offer valuable information, but waveform capnography is particularly beneficial for detailed analysis. The combination of these tools enhances the overall monitoring capabilities in EMS.
Benefits of Capnography in EMS
Enhanced Patient Monitoring
Capnography offers continuous, real-time monitoring of a patient’s respiratory status. This continuous data helps EMTs quickly identify changes in a patient’s condition. For instance, during transport, EMTs can monitor the effectiveness of interventions like oxygen therapy or ventilation. This real-time feedback is crucial in emergency settings where every second counts. By providing immediate data, capnography helps EMTs make timely adjustments to their care strategies, improving patient outcomes significantly.
Improved Decision-Making
Capnography aids in evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions during CPR. EMTs can see the CO2 levels rise and fall with each compression, indicating blood flow and ventilation. Additionally, a sudden increase in CO2 can signal the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). This early indication allows EMTs to detect ROSC even before a pulse is palpable. Furthermore, capnography helps in making critical decisions about continuing or ceasing resuscitation efforts. By providing clear, objective data, it supports more precise and effective decision-making in critical moments.
Non-Invasive Assessment
Capnography offers a non-invasive method to assess respiratory status. This approach reduces the need for more invasive procedures, which can be uncomfortable and risky for patients. For example, capnography can detect hypoventilation, apnea, airway obstruction, and hypercarbia early. These conditions might not be apparent through other means, but capnography provides immediate and clear indications. This early detection allows for prompt intervention, potentially preventing deterioration and improving patient outcomes. By reducing the need for invasive procedures, capnography also enhances patient comfort and safety.
Differentiation of Respiratory Distress Causes
Capnography helps differentiate between various causes of respiratory distress. Conditions like asthma, COPD, and CHF can present similarly, but they require different treatments. By analyzing the CO2 waveform patterns, EMTs can identify specific conditions more accurately. For example, a “shark fin” waveform might indicate bronchospasm, commonly seen in asthma. This differentiation helps tailor specific treatments, improving the effectiveness of care. Accurate diagnosis is crucial in emergency settings, where time and correct intervention are vital. Capnography enhances diagnostic accuracy, leading to better-targeted and more effective treatments.
Practical Applications in EMS
Resuscitation
Capnography plays a crucial role during resuscitation efforts. It monitors patients continuously, providing real-time data on ventilation and circulation. During CPR, capnography helps EMTs evaluate the effectiveness of chest compressions. A sudden increase in CO2 levels can indicate the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), even before a pulse is detectable. This early detection allows EMTs to respond quickly, improving the chances of successful resuscitation. Additionally, capnography provides valuable information for deciding when to continue or cease resuscitation efforts. It supports more precise and effective decision-making in critical moments.
Respiratory Emergencies
Capnography is invaluable in managing respiratory emergencies. It helps assess conditions like asthma and COPD exacerbations. For instance, capnography can detect bronchospasm by identifying the characteristic “shark fin” waveform. This detection allows EMTs to administer appropriate treatments, such as bronchodilators, more effectively. Capnography also helps manage airway obstructions by providing real-time feedback on the patient’s respiratory status. This immediate information allows for prompt interventions, improving patient outcomes. By offering detailed and continuous respiratory data, capnography enhances the management of respiratory emergencies.
General Patient Management
Capnography is not limited to critical care situations. It also plays a vital role in general patient management. For instance, it monitors sedated patients to ensure they maintain adequate ventilation. Sedation can depress respiratory function, but capnography provides continuous data, allowing EMTs to adjust care as needed. Additionally, capnography assesses non-intubated patients effectively. It provides early warning signs of respiratory compromise, allowing for timely intervention. By offering real-time, non-invasive monitoring, capnography improves overall patient care and safety in various EMS situations.
Training Requirements
EMTs must receive comprehensive education to interpret capnography readings. This training involves understanding CO2 waveforms and their clinical significance. For instance, EMTs need to recognize the “shark fin” pattern indicative of bronchospasm. Additionally, ongoing practice ensures that EMTs maintain proficiency. Regular drills and simulations help reinforce learning and keep skills sharp. Furthermore, integrating capnography training into certification programs can ensure that all EMTs possess this critical knowledge from the start.
Cost and Equipment Durability
The initial investment in capnography equipment can be significant. High-quality capnography devices, essential for accurate readings, come at a cost. Additionally, maintaining these devices incurs ongoing expenses. EMS agencies must budget for regular maintenance and calibration to ensure reliability. Equipment durability is also a concern. Capnography devices must withstand the harsh conditions of prehospital care, including temperature fluctuations and physical impacts. Agencies often face the challenge of balancing cost with the need for robust, reliable equipment.
Integration into Existing Protocols
Incorporating capnography into existing EMS protocols requires careful planning. EMS agencies must update standard operating procedures to include capnography use in various scenarios. This integration involves coordinating with EMS leadership and medical directors. They need to ensure that capnography guidelines align with overall patient care strategies. Additionally, agencies must provide clear instructions on when and how to use capnography. Protocols should specify its application in resuscitation, respiratory emergencies, and general patient management. Effective integration also requires regular review and updates to protocols based on new research and clinical findings.
Best Practices for Implementing Capnography
Training and Education
Developing a comprehensive curriculum for EMTs and paramedics is crucial. This curriculum should cover the basics of capnography, waveform interpretation, and clinical applications. Instructors should use real-world scenarios to illustrate key points. Continuous skill assessment is essential to ensure ongoing competence. Regular evaluations and refresher courses can help EMTs stay current with best practices. Moreover, integrating capnography training into certification programs can standardize knowledge across the field.
Equipment Management
Selecting durable capnography devices is a priority. EMS agencies should choose equipment known for its reliability and robustness. Regular maintenance and calibration are crucial to ensure accuracy. Agencies should establish protocols for routine equipment checks and servicing. Additionally, keeping spare parts and backup devices can minimize downtime. Proper training on equipment use and care can also extend the lifespan of capnography devices.
Protocol Development
Clear guidelines for capnography use are essential for consistent application. Protocols should detail when and how to use capnography in different situations. For example, guidelines should specify its use during CPR, for monitoring sedated patients, and in managing respiratory emergencies. Involving EMS leadership and medical directors in protocol development ensures alignment with overall patient care strategies. Regularly reviewing and updating protocols based on the latest research and clinical findings can maintain their relevance and effectiveness.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Advancements in capnography technology continue to emerge. Newer devices offer improved accuracy, portability, and ease of use. For instance, wireless capnography systems enable real-time monitoring without cumbersome cables. Innovations in data integration allow capnography readings to sync with other monitoring tools. This integration provides a comprehensive view of a patient’s status, enhancing clinical decision-making. Future developments may include enhanced AI algorithms to interpret capnography data, providing EMTs with actionable insights quickly. These advancements hold the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes.
Real-World Case Studies
Many EMS providers report success with incorporating capnography. For example, an EMS agency in California implemented capnography in all their ambulances. They reported improved patient outcomes, especially in managing respiratory distress and during resuscitations. Another case in New York highlighted the early detection of hypoventilation in a patient, allowing timely intervention and preventing further complications. These stories demonstrate the tangible benefits of capnography in enhancing patient care. They also offer valuable lessons for other EMS agencies considering its implementation.
Reflection on Capnography’s Role in EMS
Capnography significantly impacts patient care in EMS. It enhances monitoring, improves decision-making, and provides early detection of respiratory issues. These benefits contribute to the overall effectiveness of EMS, ensuring better patient outcomes. Capnography also supports the EMS mission of providing high-quality prehospital care. As technology advances, its role in EMS will likely expand, offering even greater benefits. EMS providers must stay informed about these developments and integrate them into their practices to continue delivering exceptional patient care.
Looking Ahead
The field of EMS practices evolves constantly, driven by technological advancements and research. Continuous improvement and adaptation are vital to keep pace with these changes. Capnography represents a significant step forward in EMS care, offering real-time insights into patient status. Its integration into EMS practices will continue to grow, enhancing patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Staying informed about new developments in capnography and other EMS technologies will be crucial for EMS providers. Embracing these advancements ensures that EMS agencies can provide the best possible care to their patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
Capnography in EMS offers significant benefits and helps improve patient outcomes. However, there are always more questions that arise when integrating new technology into medical practice. Below are some frequently asked questions about capnography in EMS that go beyond what was covered in the main article. These questions and answers aim to provide additional insights into the practical aspects of capnography use.
How does capnography help in monitoring sedated patients?
Capnography helps monitor respiratory function in sedated patients by providing continuous CO2 measurements. This allows EMTs to detect hypoventilation or apnea early, ensuring timely intervention. It is crucial for maintaining patient safety during sedation.
Can capnography be used in pediatric patients?
Yes, capnography can be used in pediatric patients. It provides valuable respiratory monitoring and helps detect respiratory distress early. Adjustments in the equipment and interpretation of waveforms may be necessary for pediatric use.
What are the limitations of capnography?
Capnography might not be accurate in patients with low tidal volumes or those with severe pulmonary diseases. It also requires proper calibration and maintenance to ensure accurate readings. Additionally, interpreting the waveforms correctly requires proper training.
How does capnography compare to pulse oximetry?
Capnography provides real-time information about ventilation, while pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation. Capnography can detect respiratory issues before they affect oxygen levels. Both tools complement each other for comprehensive respiratory monitoring.
References
Why Every EMS Provider Should Know About Capnography – An overview of the importance of capnography in EMS and its critical role in patient care.
The Importance of Capnography in Prehospital Care – Detailed insights into how capnography improves patient outcomes in prehospital settings.
Advancing Airway Management: Capnography in Prehospital Care – A comprehensive guide to using capnography for better airway management in EMS.
Capnography Implementation and Training in EMS – Discusses the training requirements and best practices for implementing capnography in EMS.
Capnography EMS Training – Information on EMS training programs and resources for capnography education.

Lisa VanderMeulen brings over 15 years of field experience as a licensed paramedic and firefighter in Florida. She currently serves as a Lieutenant with the Lehigh Acres Fire Control & Rescue District and as Dean of Ricky Rescue Training Academy, where she oversees curriculum development for EMT and fire service education.
Lisa holds an Associate of Science in Emergency Medical Services Technology from Florida SouthWestern State College and advanced certifications from the Florida Bureau of Fire Standards & Training, including Fire Officer II, Fire Instructor II, and Incident Safety Officer. Her licensure as a paramedic is backed by the Florida Department of Health.
In addition to her teaching and command roles, she actively serves on safety committees, community outreach programs like Fire Prevention Week and Pink Heals, and holds leadership positions within IAFF Local 1826.